linux dd hard drive speed test|Linux disk performance test : Chinese 1. dtstat. All five commands provide useful ways to view disk activity. Probably one of the easiest and most obvious of these commands is dstat. In spite of the fact that the dstat . Autoclave Service Agents NZ. Our Autoclave Service agents are trained technical support personnel that can provide servicing, validation and advice on the use of your steriliser. They .
{plog:ftitle_list}
Learn about the impact of gamma and autoclave sterilization on silicone tubing. Learn how t.
Test read speed using dd. If you apply logic and reverse the if and of parameters from the previous example, you will arrive at the following dd command testing the speed of .
I’ll show how to test the read/write speed of a disk from the Linux command line using dd command. I’ll also show how to install and use hdparm utility for measuring read .
how to check ubuntu hard drive
how to check ubuntu drive performance
dd will give you information on write speed. If the drive doesn't have a file system (and only then), use of=/dev/sda. Otherwise, mount it on /tmp and write then delete the test . Next we have our main performance test using dd. The syntax of dd is quite straightforward, but different from most other command line tools. let us look at it in some . 1. dtstat. All five commands provide useful ways to view disk activity. Probably one of the easiest and most obvious of these commands is dstat. In spite of the fact that the dstat . To test the write speed, we can run the dd command and set the input file to /dev/zero. Then, we write the stream of zeros from the /dev/zero onto the /tmp/tempfile: $ dd if .
Here's several methods for testing I/O performance on GNU/Linux ranging from irrelevant tools like dd that are utterly worthless for this purpose to actually useful ways to determine a drives . Use DD command on Linux to test read speed. Before testing the first flush caches data, use the following command- $ echo 3 | sudo tee /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches. time time dd . The dd command is a built-in Linux tool primarily used for converting and copying files. To measure write speed, you can use the following command: dd if=/dev/zero. Use dd command to monitor the reading and writing performance of a disk device: Open a shell prompt. Or login to a remote server via ssh. Use the dd command to measure server throughput (write speed): # dd if= /dev/zero of= /tmp/test1.img bs=1G count=1 oflag=dsync
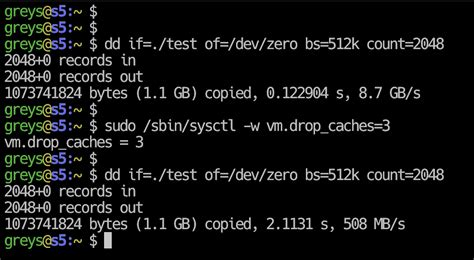
Test read speed using dd. If you apply logic and reverse the if and of parameters from the previous example, you will arrive at the following dd command testing the speed of reading from ./test file: greys@s5:~ $ dd if=./test of=/dev/zero bs=512k count=2048 oflag=direct. I’ll show how to test the read/write speed of a disk from the Linux command line using dd command. I’ll also show how to install and use hdparm utility for measuring read speed of a disk on Linux Mint, Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, RHEL. dd will give you information on write speed. If the drive doesn't have a file system (and only then), use of=/dev/sda. Otherwise, mount it on /tmp and write then delete the test output file. dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/output bs=8k count=10k; rm -f /tmp/output. 10240+0 records in. 10240+0 records out. 83886080 bytes (84 MB) copied, 1.08009 s, 77.7 MB/s
Next we have our main performance test using dd. The syntax of dd is quite straightforward, but different from most other command line tools. let us look at it in some detail: if=/dev/zero: Use the /dev/zero device as input file; of=/tmp/mnt/temp: Use the ‘temp’ file, located on the partition(/disk) we just mounted under /tmp/mnt as the . 1. dtstat. All five commands provide useful ways to view disk activity. Probably one of the easiest and most obvious of these commands is dstat. In spite of the fact that the dstat command begins . To test the write speed, we can run the dd command and set the input file to /dev/zero. Then, we write the stream of zeros from the /dev/zero onto the /tmp/tempfile: $ dd if =/dev/zero of=/tmp/tempfile bs=1M count=1024 conv=fdatasync. 1024+0 records in. .
Here's several methods for testing I/O performance on GNU/Linux ranging from irrelevant tools like dd that are utterly worthless for this purpose to actually useful ways to determine a drives real-world performance. Use DD command on Linux to test read speed. Before testing the first flush caches data, use the following command- $ echo 3 | sudo tee /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches. time time dd if=/path/to/bigfile of=/dev/null bs=8k. Run the following command to test the data with cache- tp@linux:~$ dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/laptop.bin bs=1G count=1 oflag=direct. The dd command is a built-in Linux tool primarily used for converting and copying files. To measure write speed, you can use the following command: dd if=/dev/zero. Use dd command to monitor the reading and writing performance of a disk device: Open a shell prompt. Or login to a remote server via ssh. Use the dd command to measure server throughput (write speed): # dd if= /dev/zero of= /tmp/test1.img bs=1G count=1 oflag=dsync
dd test write speed
Test read speed using dd. If you apply logic and reverse the if and of parameters from the previous example, you will arrive at the following dd command testing the speed of reading from ./test file: greys@s5:~ $ dd if=./test of=/dev/zero bs=512k count=2048 oflag=direct. I’ll show how to test the read/write speed of a disk from the Linux command line using dd command. I’ll also show how to install and use hdparm utility for measuring read speed of a disk on Linux Mint, Ubuntu, Debian, CentOS, RHEL. dd will give you information on write speed. If the drive doesn't have a file system (and only then), use of=/dev/sda. Otherwise, mount it on /tmp and write then delete the test output file. dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/output bs=8k count=10k; rm -f /tmp/output. 10240+0 records in. 10240+0 records out. 83886080 bytes (84 MB) copied, 1.08009 s, 77.7 MB/s Next we have our main performance test using dd. The syntax of dd is quite straightforward, but different from most other command line tools. let us look at it in some detail: if=/dev/zero: Use the /dev/zero device as input file; of=/tmp/mnt/temp: Use the ‘temp’ file, located on the partition(/disk) we just mounted under /tmp/mnt as the .
1. dtstat. All five commands provide useful ways to view disk activity. Probably one of the easiest and most obvious of these commands is dstat. In spite of the fact that the dstat command begins . To test the write speed, we can run the dd command and set the input file to /dev/zero. Then, we write the stream of zeros from the /dev/zero onto the /tmp/tempfile: $ dd if =/dev/zero of=/tmp/tempfile bs=1M count=1024 conv=fdatasync. 1024+0 records in. .
Here's several methods for testing I/O performance on GNU/Linux ranging from irrelevant tools like dd that are utterly worthless for this purpose to actually useful ways to determine a drives real-world performance.
Use DD command on Linux to test read speed. Before testing the first flush caches data, use the following command- $ echo 3 | sudo tee /proc/sys/vm/drop_caches. time time dd if=/path/to/bigfile of=/dev/null bs=8k. Run the following command to test the data with cache- tp@linux:~$ dd if=/dev/zero of=/tmp/laptop.bin bs=1G count=1 oflag=direct.
check disk performance Linux
Linux test hard disk speed
Linux test drive speed
Linux ssd benchmark tool
Prions can be deactivated in a steam autoclave using a temperature of 270 °F (132 °C) at 21 psi for 90 minutes. If the prion infected material is in a solution of sodium .
linux dd hard drive speed test|Linux disk performance test